“针”听植物:植物信号分子检测
植物信号分子如过氧化氢(H2O2)、生长素(IAA)、水杨酸(SA)、细胞分裂素(ZT)、脱落酸(ABA)和茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)等在调控植物的生长发育、应对生物和非生物胁迫以及植物再生中发挥重要的调控作用。如何实时原位的获得植物信号分子的动态信息,一直是植物生物学研究面临的难题。“针”听植物:植物信号分子检测,让您能够“听懂”植物的“话语”,原位、实时检测不同植物信号分子在植物体内的动态变化。
技术特点:原位、实时的监测
植物信号分子检测服务,采用了先进的电化学传感器技术,能够对植物进行原位、实时、单个体的分析,在快保证灵敏度的同时,操作简单便捷。

服务选择:多样化的选择
我们的植物信号分子检测针对植物的不同部位具有不同的选择,能够满足不同用户的需求:
服务选择:多样化的选择
我们的植物信号分子检测针对植物的不同部位具有不同的选择,能够满足不同用户的需求:
(1)以平板电极为基底的电化学传感器
适用于扁平状、面积较大的植物部位的检测,如叶片等。这种传感器设计扁平,能够紧密贴合植物叶片,实现低损检测,进行高效的信号分子检测。
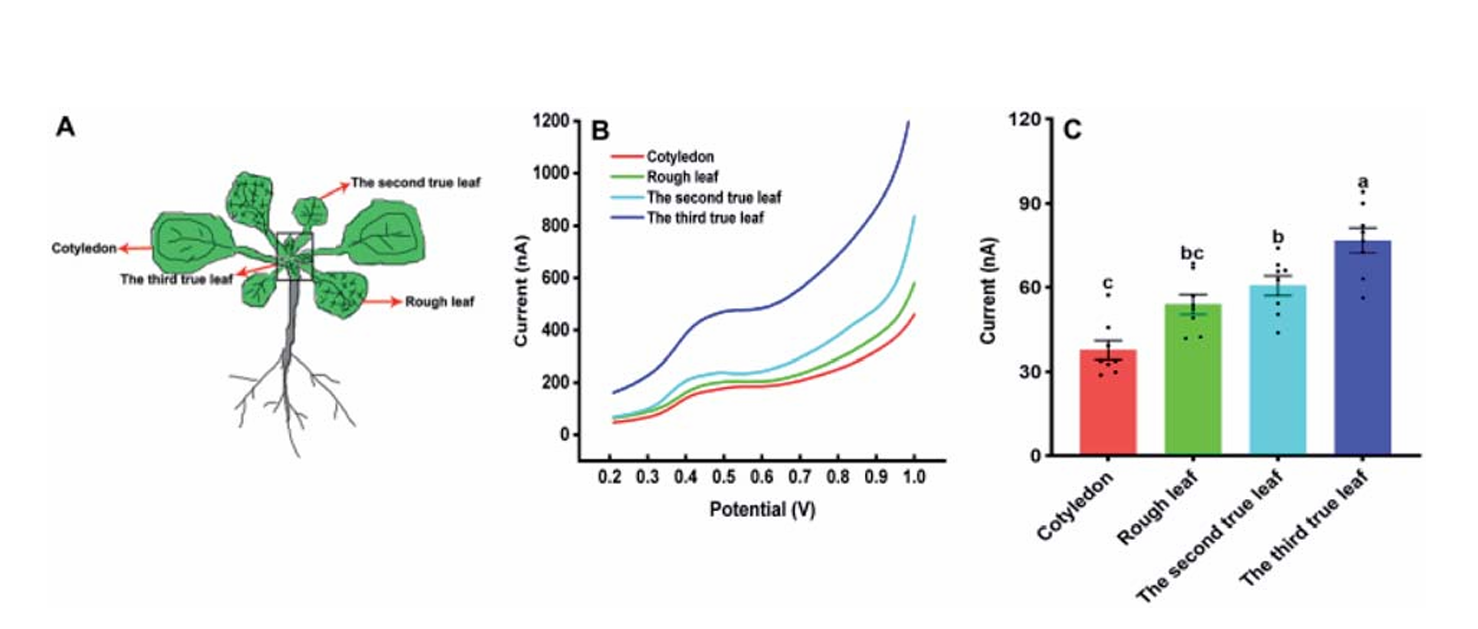
(2)以针状电极为基底的电化学传感器
针对植物根、茎等微小、脆弱部位,我们的针状电极传感器能够实现微损检测。这种传感器设计精细,对植物的损伤极小,同时保证了检测的准确性。
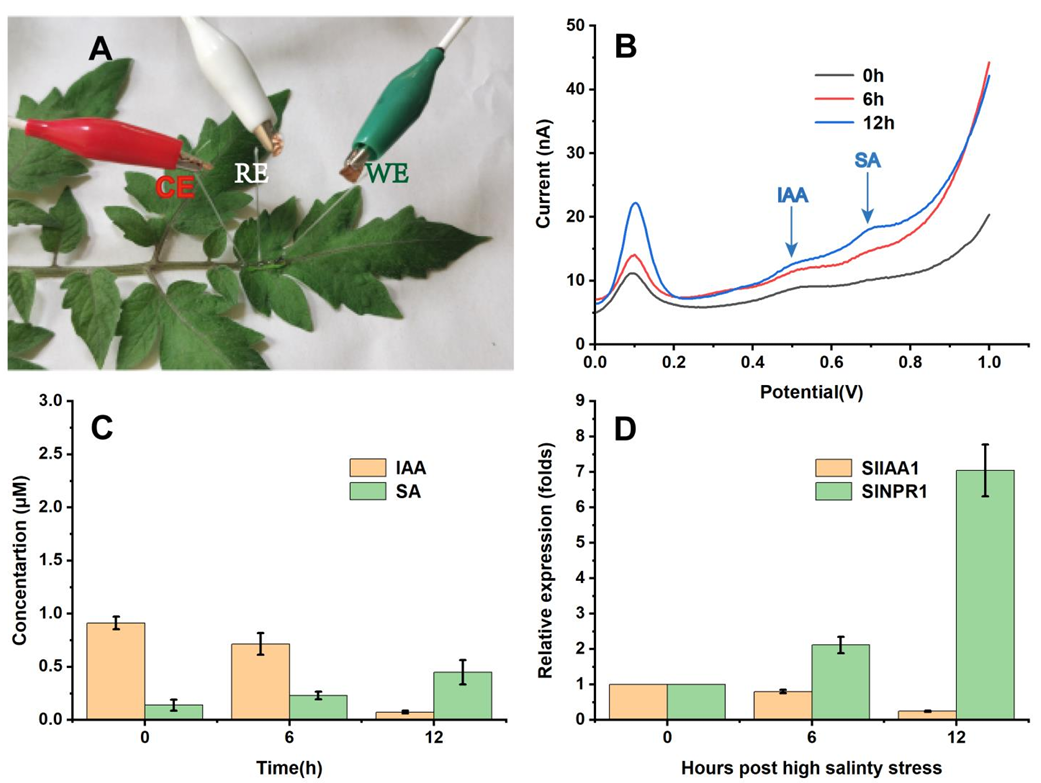
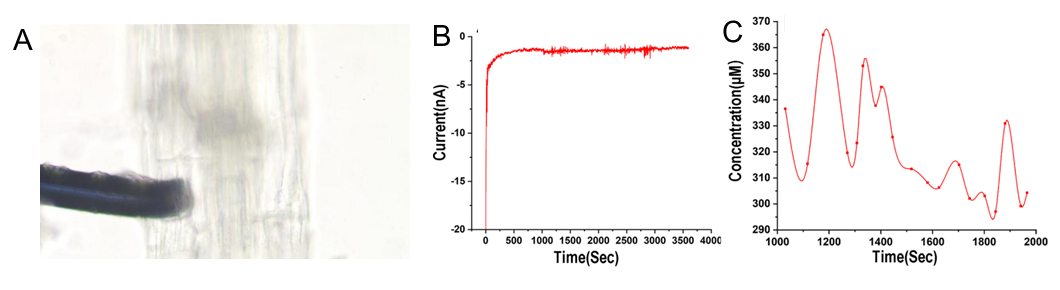
(3)以超微电极为基底的电化学传感器
对于需要更精细检测的用户,我们提供了微电极电化学传感器。这种传感器可用于检测植物细胞,如气孔微区等,为植物细胞层面的研究提供了强有力的工具。
竞品比较:优势满满、超值选择
目前多用气相色谱-质谱法(GC-MS)、液相色谱-质谱法(LC-MS)和高效液相色谱法(HPLC-MS/MS)等方法检测植物信号分子,但它们受到复杂和耗时的样品预处理步骤的限制,而且复杂的样品处理过程会导致植物信号分子受到损失。更此外,复杂的样品处理往往需要大量的植物样品,需要的时间也更长
而我们的服务能够实现原位、实时检测,操作简单便捷,出结果快,且价格适中。
技术支持
我们的技术距今已有十年发展历程,技术简单便捷,应用范围广阔,检测结果稳定。目前我们已通过此项技术发表文章19篇, 包括:
- 1.Zhang et al,Wearable electrochemical immunosensor based on ultra-thin flexible stainless steel sheets for detection of methyl jasmonate in tomato leaves, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2025, 288,117853
- 2.Zhang et al., Smartphone-based electrochemical microsensor in combination with internet of things for remote monitoring of salicylic acid in plant, Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2025, 287, 117733
- 3.Liu, et al. Electrochemical sensors for plant signaling molecules. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2025, 267:116757
- 4.Yant et al. AuNPs/GO/Pt microneedle electrochemical sensor for in situmonitoring of hydrogen peroxide in tomato stems in response to wounding stimulation. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2025, 417:1067-1079
- 5.Tang, et al. Microneedle electrochemical sensor based on disposable stainless-steel wire for real-time analysis of indole-3-acetic acid and salicylic acid in tomato leaves infected by Pst DC3000 in situ. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2024, 342875
- 6.You, et al. An ultrasensitive probe-free electrochemical immunosensor for gibberellins employing polydopamine-antibody nanoparticles modified electrode. Bioelectrochemistry, 2023, 108331
- 7.Tang, et al. Continuous In Vivo Monitoring of Indole-3-Acetic Acid and Salicylic Acid in Tomato Leaf Veins Based on an Electrochemical Microsensor. Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;13(12):1002
- 8.Huo, et al. Disposable Stainless-Steel Wire-Based Electrochemical Microsensor for In Vivo Continuous Monitoring of Hydrogen Peroxide in Vein of Tomato Leaf. Biosensors 2022, 12, 35
- 9.Sun, et al. Disposable stainless steel working electrodes for sensitive and simultaneous detection of indole-3-acetic acid and salicylic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves under biotic stresses. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2022, 414:7721-7730
- 10.Sun, et al. Rapid mapping of the IAA in leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana using a simple paper-based electroanalytical device coupled with microsampling. RSC Adv 2021, 11, 30392–30397
- 11.Sun, et al. Paper-Based Analytical Devices for the Rapid and Direct Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide in Tomato Leaves Inoculated with Botrytis cinerea. Sensors (Basel). 2020, 20(19): E5512
- 12.He, et al. Digitalized pencil trace modified electrodes for real time evaluation of salicylic acid in detached Arabidopsis thaliana leaves during regeneration, Analytica Chimica Acta 2020, 1120:59-66
- 13.Wang, et al. Real time sensing of salicylic acid in infected tomato leaves using carbon tape electrodes modified with handed pencil trace, Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical 2019, 286: 104–110
- 14.Sun, et al. Electrochemical mapping of indole-3-acetic acid and salicylic acid in whole pea seedlings under normal conditions and salinity, Sensors & Actuators: B. Chemical 2018, 276: 545–551
- 15.Sun, et al. Paper-based analytical devices for direct electrochemical detection of free IAA and SA in plant samples with the weight of several milligrams, Sensor Actuat. B Chem., 2017, 247: 336-342
- 16.Sun, et al. Paper-based electroanalytical devices for in situ determination of salicylic acid in living tomato leaves. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2014, 60:154-160
应用案例
自从我们的服务上线以来,已经为多位合作者提供植物信号检测的技术服务,所获得的植物信号实时变化的数据,为他们的研究带来了新的视角,以下为一些代表性的发表文章:
- 15.Liu, et al. Genome and transcriptome of Selaginella kraussiana reveal evolution of root apical meristems in vascular plants, Current Biology 2023, 33(19), 4085-4097.e5
- 16.Liu, et al. Transcriptional landscapes of de novo root regeneration from detached Arabidopsis leaves revealed by time-lapse and single-cell RNA sequencing analyses. Plant communications 2022, 3, 100306
- 17.Ye, et al. AP2/ERF Transcription Factors Integrate Age and Wound Signals for Root Regeneration. Plant cell 2020, 32:226-241
- 18.Zhang, et al. Jasmonate-mediated wound signaling promotes plant regeneration. Nature Plants 2019, 491-497
- 19.Pan, et al. Control of De Novo Root Regeneration Efficiency by Developmental Status of Arabidopsis Leaf Explants, Journal of Genetics and Genomics 2019,46:133-134
结束语
植物信号分子检测服务,让您与植物的“对话”变得更加直接和深入。我们相信,这项服务将成为您科研道路上的得力助手,联系地址:南通大学生命科学学院18号楼C509,联系人:孙老师(13585224878),快来开启您的植物信号分子检测之旅吧!



